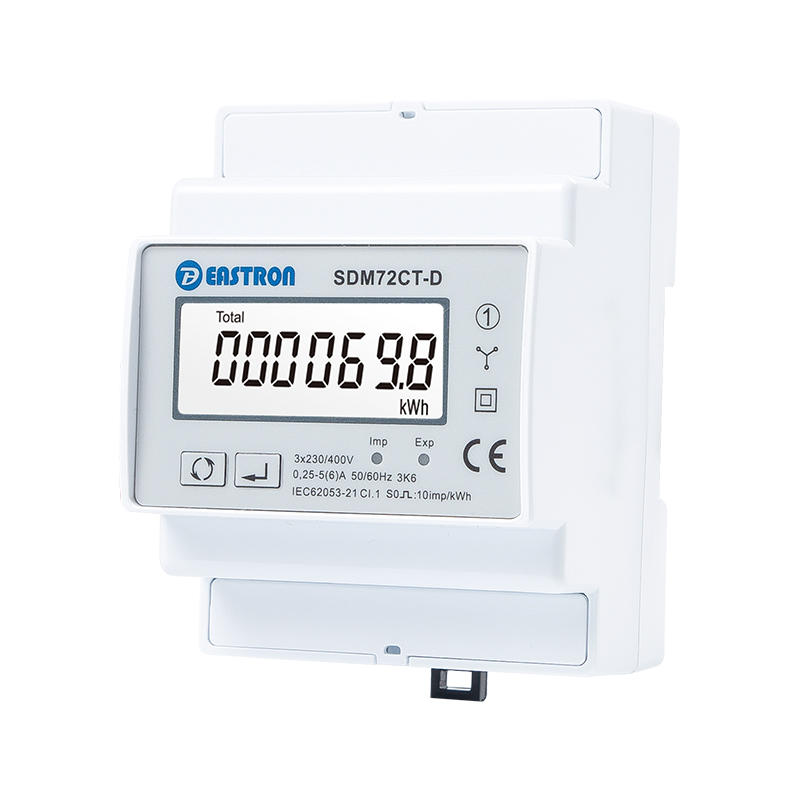
3P4W, 5A CT, 3x230/400V AC
LCD kWh Meter
Pulse Output

3P4W, 5A CT, 3x230/400V AC
LCD kWh Meter
Pulse Output
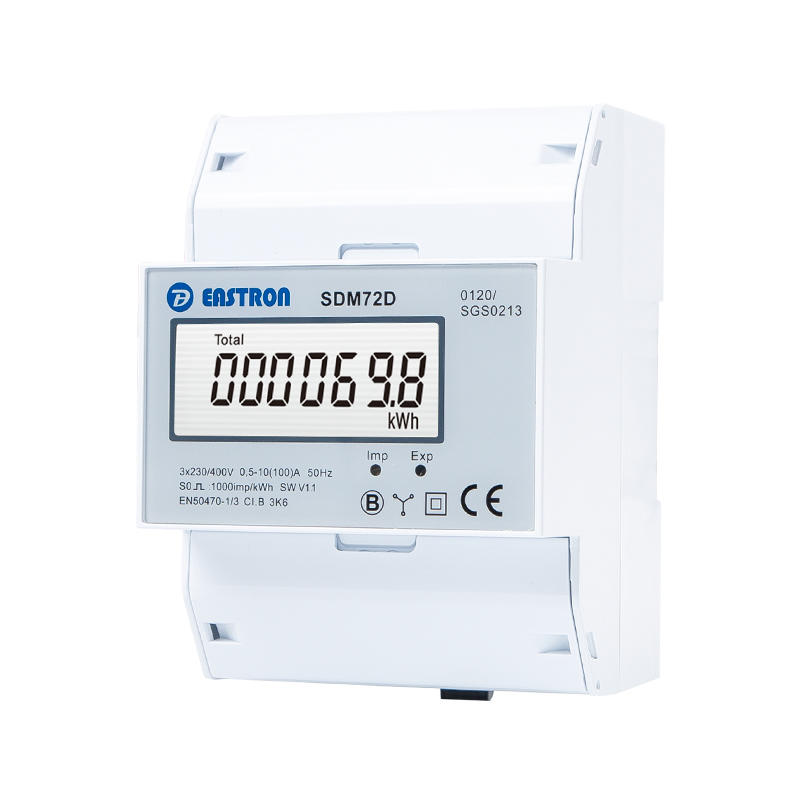

3P4W, 100A, 3x230/400V AC
LCD kWh Meter
Pulse Output
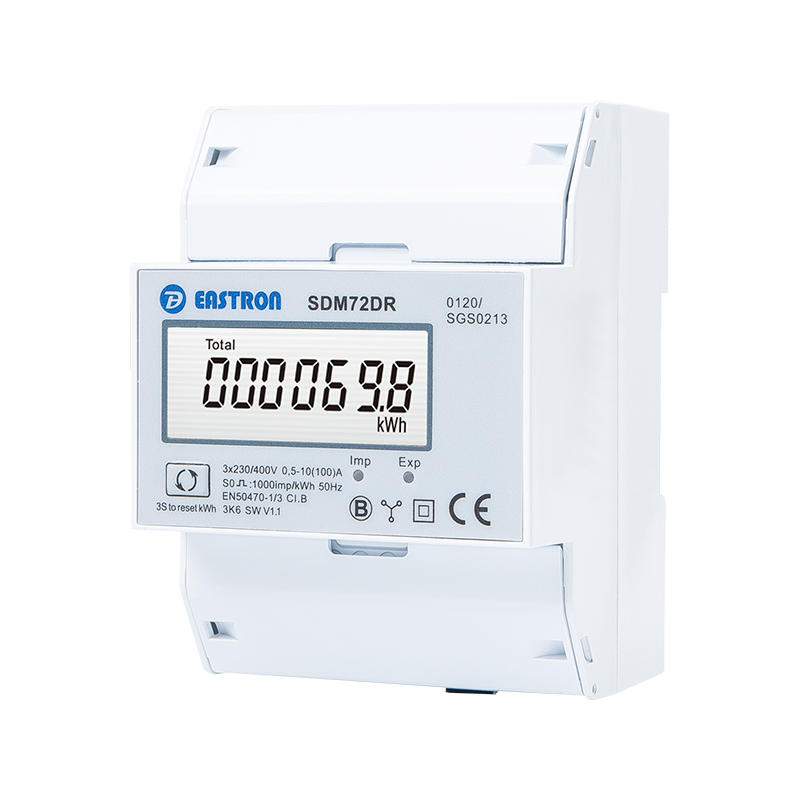

3P4W, 100A, 3x230/400V AC
LCD Energy Meter
Pulse Output
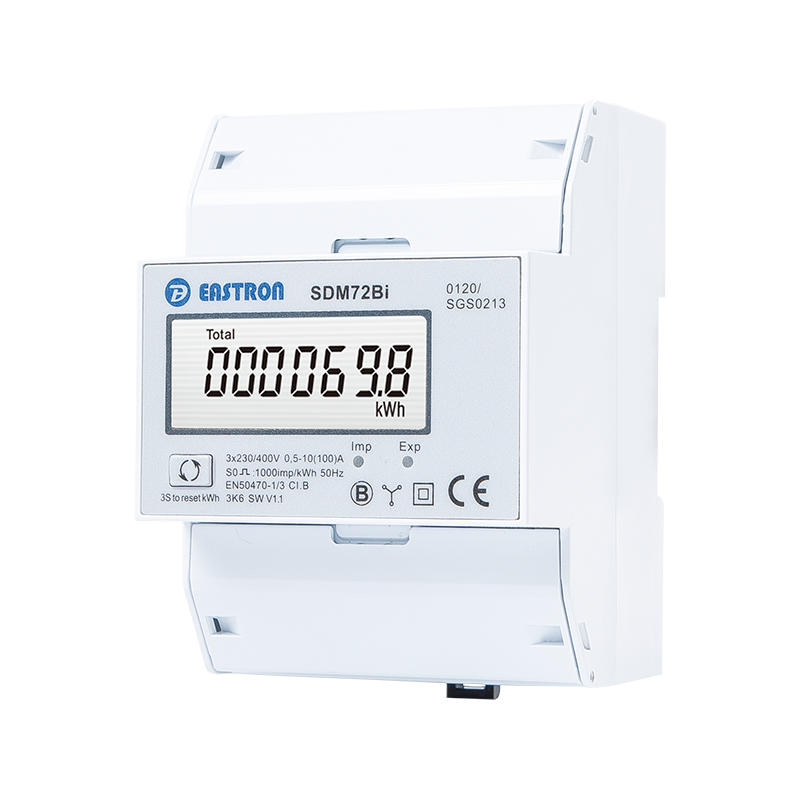

3P4W, 100A, 3x230/400V AC
Bi-directional Energy Meter
Pulse Output
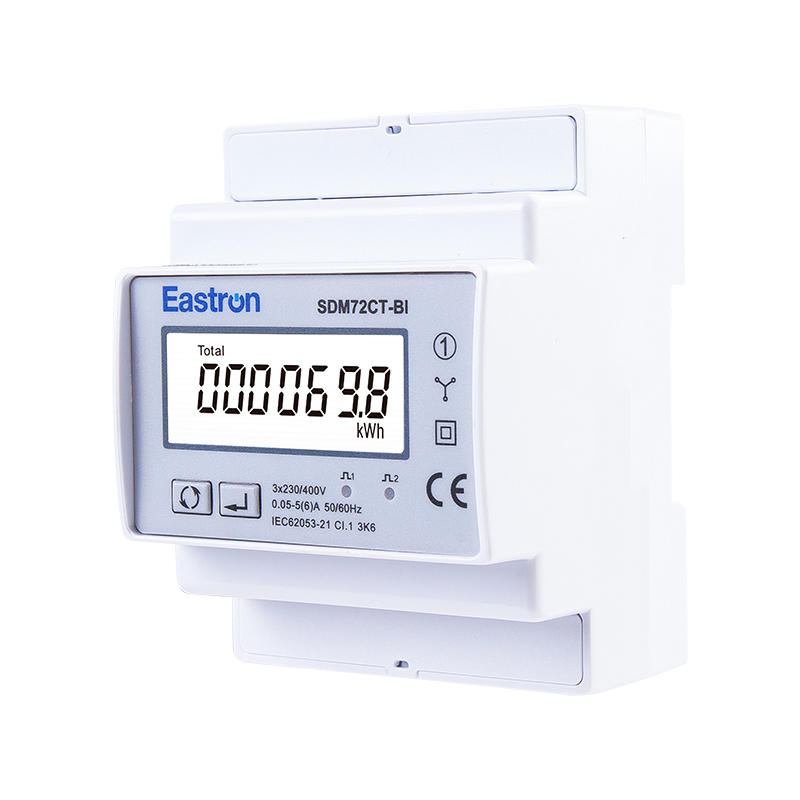

3P4W, 5A CT, 3x230/400V
LCD Bi-directional Meter
Pulse Output
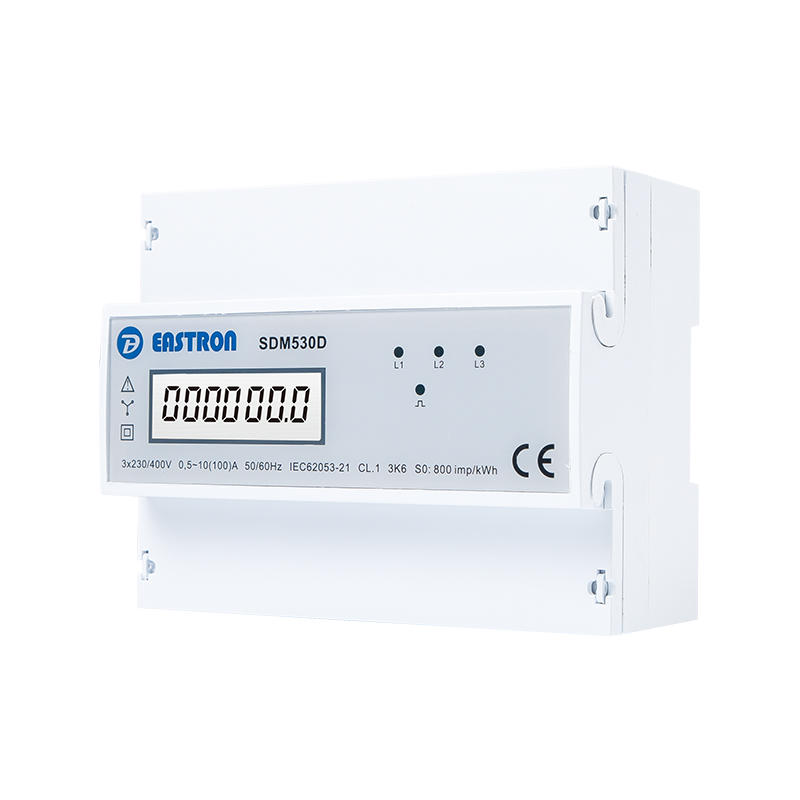

3P4W, 100A, 3X230/400V
LCD kWh Meter
Pulse Output
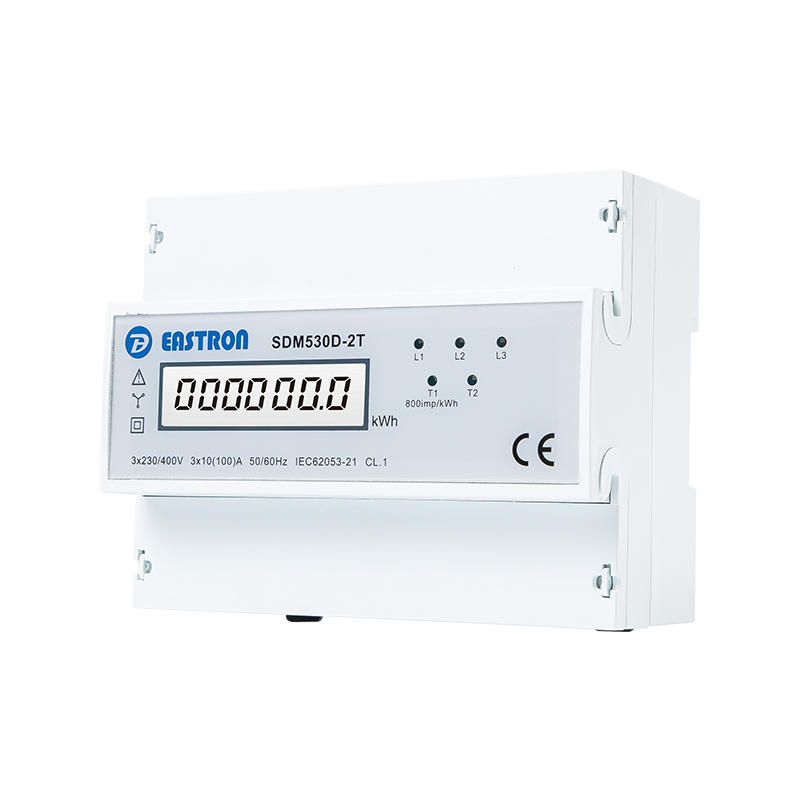

3P4W, 100A, 3X230/400V
LCD kWh Meter, Dual Source
Pulse Output

1P2W/3P3W/3P4W
Easy Connection Solution
Wi-Fi & RS485 Modbus RTU

1P2W/3P3W/3P4W
Easy Connection Solution
RS485 Modbus RTU
Eastron Electronic Co., Ltd. headquartered in Jiaxing, China, near to Shanghai, Hangzhou, Jiangsu, is one of the leading high-tech manufacturer and supplier for electricity products and energy measurement solutions. Over the years, we have developed a rich range of electricity meters, sensors, communication modules and management systems.
Eastron keeps investing on the research and development of new technology and new products on electricity metering. We have energetic and innovative development teams in both China and UK,which help us keep the competitive edge in the market. Three Phase Electronic kWh meter Suppliers and Wholesale Three Phase Electronic kWh meter Factory in China.The collaboration with leading universities and institutions also brings many cutting-edge technology into our products. To make sure the reliability of the products, Eastron has setup own professional lab that can performs EMC, LVD, accuracy and environment tests according to IEC, EN, GB, UL standards.
With more than 40 patented technologies on software, embedded software and hardware, Eastron has been awarded with “High-tech Enterprise” and “High-tech R&D Centre of Electricity Application”. Eastron strictly follows ISO 9001 Quality management system, and the production is approved by SGS according to MID standard. Supply Wholesale Three Phase Electronic kWh meter for sale.
Creating value to and growing up with our partners is our mission. Eastron provides not only the high quality and innovative products, but also first-class service to all our customers. We have professional team for technical supports and aftersales services. We have provided products and services to more than 50 countries in Europe, Asia-Pacific, America, Middle East, and Africa. We pride ourselves on having long-term partners globally that allows us to further our growth and bring our innovation and quality to the market.